A GraphicsLayer contains one or more client-side Graphics. Each graphic in the GraphicsLayer is rendered in a LayerView inside either a SceneView or a MapView. The graphics contain discrete vector geometries that represent real-world phenomena.
Unlike FeatureLayer and MapImageLayer, a GraphicsLayer has no schema. Therefore, the graphics that compose a GraphicsLayer may be of more than one geometry type (either points, lines, or polygons). Each graphic must have its own symbol since the GraphicsLayer cannot have an associated renderer. Graphics may also contain different attribute schema from one another.
It is generally preferred to construct a FeatureLayer with its source property when working with client-side graphics since the FeatureLayer has more capabilities than the GraphicsLayer, including rendering, querying, and labeling.
Graphics can be added to an instance of GraphicsLayer in several ways. They may be added via the add() method, directly on the graphics property in the constructor, or after the instance is created. Use Map.add() to add a GraphicsLayer to a Map instance.
require(["esri/layers/GraphicsLayer", "esri/Graphic"], function(GraphicsLayer, Graphic){
// Create graphics
var graphicA = new Graphic(); // graphic with line geometry
var graphicB = new Graphic(); // graphic with point geometry
var graphicC = new Graphic(); // graphic with polygon geometry
var graphicD = new Graphic();
var graphicE = new Graphic();
// Add graphic when GraphicsLayer is constructed
var layer = new GraphicsLayer({
graphics: [graphicA]
});
// Add graphic to graphics collection
layer.graphics.add(graphicB);
// Add graphic using add()
layer.add(graphicC);
layer.addMany([graphicD, graphicE]);
// Add GraphicsLayer to map
map.add(layer);
});
The MapView and SceneView each contain a graphics collection that may be used in place of a GraphicsLayer.
An instance of this class is also a Promise. This allows you to execute code once the promise resolves, or when the layer finishes loading its resources. See then() for additional details.
Constructors
new GraphicsLayer(properties)
properties Object See the properties for a list of all the properties that may be passed into the constructor. |
Property Overview
| Name | Type | Summary | |
|---|---|---|---|
| String | The name of the class. more details | more details | |
| Object | Specifies how graphics are placed on the vertical axis (z). more details | more details | |
| Extent | The full extent of the layer. more details | more details | |
| Collection | A collection of graphics in the layer. more details | more details | |
| String | The unique ID assigned to the layer. more details | more details | |
| String | Indicates how the layer should display in the LayerList widget. more details | more details | |
| Boolean | Indicates whether the layer instance has loaded. more details | more details | |
| Error | The Error object returned if an error occurred while loading. more details | more details | |
| String | Represents the status of a load operation. more details | more details | |
| Object[] | A list of warnings which occurred while loading. more details | more details | |
| Number | The maximum scale at which the layer is visible in the view. more details | more details | |
| Number | The minimum scale at which the layer is visible in the view. more details | more details | |
| Number | The opacity of the layer. more details | more details | |
| Boolean | Apply perspective scaling to screen-size point symbols in a SceneView. more details | more details | |
| String | The title of the layer used to identify it in places such as the Legend and LayerList widgets. more details | more details | |
| String | For GraphicsLayer the type is | more details | |
| Boolean | Indicates if the layer is visible in the View. more details | more details | |
Property Details
declaredClassStringreadonly
The name of the class. The declared class name is formatted as
esri.folder.className.elevationInfoObject
Specifies how graphics are placed on the vertical axis (z). This property only has an effect in a SceneView. See the ElevationInfo sample for an example of how this property may be used.
Properties:mode StringDefines how the graphic is placed with respect to the terrain surface. If the geometry consists of multiple points (e.g. lines or polygons), the elevation is evaluated separately for each point. See the table below for a list of possible values.
Mode Description on-the-ground Graphics are placed on the terrain surface. relative-to-ground The graphic is placed at an elevation relative to the terrain surface. The graphic's elevation is determined by summing up the terrain elevation, the offsetvalue and the geometry's z-value (if present).absolute-height Graphics are placed at an absolute height above sea level. This height is determined by summing up the offsetvalue and the geometry's z-value (if present). It doesn't take the elevation of the terrain into account.relative-to-scene Graphics are aligned to buildings and other objects part of 3D Object SceneLayer or IntegratedMeshLayer, depending on which has higher elevation. If the graphic is not directly above a building or any other feature, it is aligned to the terrain surface elevation. If present, z-values will be ignored. optionaloffset NumberAn elevation offset in meters, which is added to the vertical position of the graphic. When
mode = "on-the-ground", this property has no effect.The full extent of the layer. By default, this is worldwide. This property may be used to set the extent of the view to match a layer's extent so that its features appear to fill the view. See the sample snippet below.
Example:// Once the layer loads, set the view's extent to the layer's fullextent layer.then(function(){ view.extent = layer.fullExtent; });graphicsCollection autocast
A collection of graphics in the layer. Each graphic is a vector representation of the location of a real-world feature. Each graphic in a single GraphicsLayer may contain either a Point, Polyline, or Polygon geometry. In addition, each Graphic in the collection may contain its own attributes, Symbol, and PopupTemplate.
To add a graphic to the GraphicsLayer use add(), or GraphicsLayer.graphics.add().
- See also:
Example:// Add graphics to GraphicsLayer directly as an array layer.graphics = [graphicA, graphicB]; // Add graphics to layer via Collection layer.graphics.addMany([graphicC, graphicD]);idString
The unique ID assigned to the layer. If not set by the developer, it is automatically generated when the layer is loaded.
listModeString
Indicates how the layer should display in the LayerList widget. The known values are listed below.
Value Description show The layer is visible in the table of contents. hide The layer is hidden in the table of contents. hide-children If the layer is a GroupLayer, hide the children layers from the table of contents. Default Value: showloadedBooleanreadonly
Indicates whether the layer instance has loaded. When
true, all the properties of the object can be accessed.Default Value: falseloadErrorErrorreadonly
The Error object returned if an error occurred while loading.
Default Value: nullloadStatusStringreadonly
Represents the status of a load operation.
Value Description not-loaded The object's resources have not loaded. loading The object's resources are currently loading. loaded The object's resources have loaded without errors. failed The object's resources failed to load. See loadError for more details. Default Value: not-loadedloadWarningsObject[]readonly
A list of warnings which occurred while loading.
maxScaleNumber
The maximum scale at which the layer is visible in the view. If the map is zoomed in beyond this scale, the layer will not be visible. A value of
0means the layer does not have a maximum scale.Default Value: 0Examples://The layer will not be visible when the //view is zoomed beyond a scale of 1:1,000 layer.maxScale = 1000;//The layer's visibility is not restricted to a maximum scale. layer.maxScale = 0;minScaleNumber
The minimum scale at which the layer is visible in the view. If the map is zoomed out beyond this scale, the layer will not be visible. A value of
0means the layer does not have a minimum scale.Default Value: 0Examples://The layer will not be visible when the view //is zoomed beyond a scale of 1:3,000,000 layer.minScale = 3000000;//The layer's visibility is not restricted to a minimum scale. layer.minScale = 0;opacityNumber
The opacity of the layer. This value can range between
1and0, where0is 100 percent transparent and1is completely opaque.Default Value: 1Example:// Makes the layer 50% transparent layer.opacity = 0.5;screenSizePerspectiveEnabledBoolean
Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.4Apply perspective scaling to screen-size point symbols in a SceneView. When
true, screen sized objects such as icons, labels or callouts integrate better in the 3D scene by applying a certain perspective projection to the sizing of features. This only applies when using a SceneView.layer.screenSizePerspectiveEnabled = true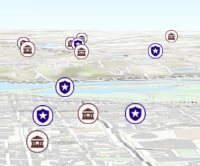
layer.screenSizePerspectiveEnabled = false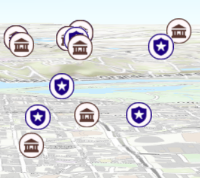
Known Limitations
Screen size perspective is currently not optimized for situations where the camera is very near the ground, or for scenes with point features located far from the ground surface. In these cases it may be better to turn off screen size perspective.
Default Value: truetitleString
typeStringreadonly
For GraphicsLayer the type is
graphics.visibleBoolean
Indicates if the layer is visible in the View. When
false, the layer may still be added to a Map instance that is referenced in a view, but its features will not be visible in the view.Default Value: trueExample:// The layer is no longer visible in the view layer.visible = false;
Method Overview
| Name | Return Type | Summary | |
|---|---|---|---|
Adds a graphic to the layer. more details | more details | ||
Adds an array of graphics to the layer. more details | more details | ||
| Promise | An instance of this class is a Promise. more details | more details | |
Cancels a load() operation if it is already in progress. more details | more details | ||
| Boolean | Indicates whether there is an event listener on the instance that matches the provided event name. more details | more details | |
| Boolean | An instance of this class is a Promise. more details | more details | |
| Boolean | An instance of this class is a Promise. more details | more details | |
| Boolean | An instance of this class is a Promise. more details | more details | |
| Promise | Loads the resources referenced by this class. more details | more details | |
| Object | Registers an event handler on the instance. more details | more details | |
| Promise | An instance of this class is a Promise. more details | more details | |
Removes a graphic from the layer. more details | more details | ||
Clears all the graphics from the layer. more details | more details | ||
Removes an array of graphics from the layer. more details | more details | ||
| Promise | An instance of this class is a Promise. more details | more details | |
Method Details
add(graphic)
Adds a graphic to the layer.
Parameter:graphic GraphicThe graphic to add to the layer.
addMany(graphics)
Adds an array of graphics to the layer.
Parameter:graphics Graphic[]The graphic(s) to add to the layer.
An instance of this class is a Promise. Therefore
always()may be used to execute a function if the promise is rejected or resolved. The input function will always execute no matter the response. For more information about promises, see the Working with Promises guide page.Parameter:optionalcallbackOrErrback FunctionThe function to execute when the promise is rejected or resolved.
Returns:Type Description Promise Returns a new promise for the result of callbackOrErrback.Example:// Although this example uses MapView, any class instance that is a promise may use always() in the same way var view = new MapView(); view.always(function(){ // This function will always execute whether or not the promise is resolved or rejected });cancelLoad()inherited
Cancels a load() operation if it is already in progress.
Indicates whether there is an event listener on the instance that matches the provided event name.
Parameter:type StringThe name of the event.
Returns:Type Description Boolean Returns true if the class supports the input event. An instance of this class is a Promise. Therefore
isFulfilled()may be used to verify if the promise is fulfilled (either resolved or rejected). If it is fulfilled,truewill be returned. See the Working with Promises guide page for more information about promises.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether the promise has been fulfilled (either resolved or rejected). An instance of this class is a Promise. Therefore
isRejected()may be used to verify if the promise is rejected. If it is rejected,truewill be returned. See the Working with Promises guide page for more information about promises.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether the promise has been rejected. An instance of this class is a Promise. Therefore
isResolved()may be used to verify if the promise is resolved. If it is resolved,truewill be returned. See the Working with Promises guide page for more information about promises.Returns:Type Description Boolean Indicates whether the promise has been resolved. Loads the resources referenced by this class. This method automatically executes for a View and all of the resources it references in Map if the view is constructed with a map instance.
This method must be called by the developer when accessing a resource that will not be loaded in a View.
Returns:Type Description Promise Resolves when the resources have loaded. Registers an event handler on the instance. Call this method to hook an event with a listener. See the Events summary table for a list of listened events.
Parameters:type StringThe name of event to listen for.
listener FunctionThe function to call when the event is fired.
Returns:Type Description Object Returns an event handler with a remove()method that can be called to stop listening for the event.Property Type Description remove Function When called, removes the listener from the event. - See also:
Example:view.on("click", function(event){ // event is the event handle returned after the event fires. console.log(event.mapPoint); });An instance of this class is a Promise. Use
otherwise()to call a function once the promise is rejected.Parameter:optionalerrback FunctionThe function to execute when the promise fails.
Returns:Type Description Promise Returns a new promise for the result of errback.Example:// Although this example uses MapView, any class instance that is a promise may use otherwise() in the same way var view = new MapView(); view.otherwise(function(error){ // This function will execute if the promise is rejected due to an error });remove(graphic)
Removes a graphic from the layer.
Parameter:graphic GraphicThe graphic to remove from the layer.
removeAll()
Clears all the graphics from the layer.
removeMany(graphics)
Removes an array of graphics from the layer.
Parameter:graphics Graphic[]The graphics to remove from the layer.
An instance of this class is a Promise. Therefore
then()may be leveraged once an instance of the class is created. This method takes two input parameters: acallbackfunction and anerrbackfunction. Thecallbackexecutes when the promise resolves (when the instance of the class loads). Theerrbackexecutes if the promise fails. See the Working with Promises guide page for additional details.Parameters:optionalcallback FunctionThe function to call when the promise resolves.
optionalerrback FunctionThe function to execute when the promise fails.
optionalprogback FunctionThe function to invoke when the promise emits a progress update.
Returns:Type Description Promise Returns a new promise for the result of callbackthat may be used to chain additional functions.Example:// Although this example uses MapView, any class instance that is a promise may use then() in the same way var view = new MapView(); view.then(function(){ // This function will execute once the promise is resolved }, function(error){ // This function will execute if the promise is rejected due to an error });
Event Overview
| Name | Type | Summary | |
|---|---|---|---|
{view: View,layerView: LayerView} | Fires after the layer's LayerView is created and rendered in a view. more details | more details | |
{view: View,layerView: LayerView} | Fires after the layer's LayerView is destroyed and no longer renders in a view. more details | more details | |
Event Details
layerview-createinherited
Fires after the layer's LayerView is created and rendered in a view.
- See also:
Properties:view ViewThe view in which the
layerViewwas created.layerView LayerViewThe LayerView rendered in the view representing the layer in
layer.Example:// This function will fire each time a layer view is created for this // particular view. layer.on("layerview-create", function(event){ // The LayerView for the layer that emitted this event event.layerView; });layerview-destroyinherited
Fires after the layer's LayerView is destroyed and no longer renders in a view.